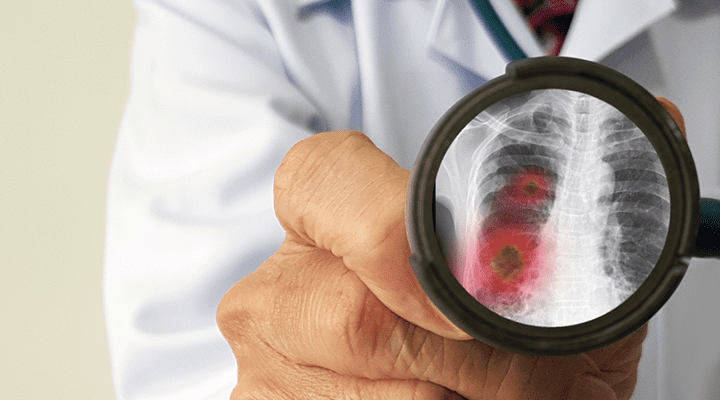
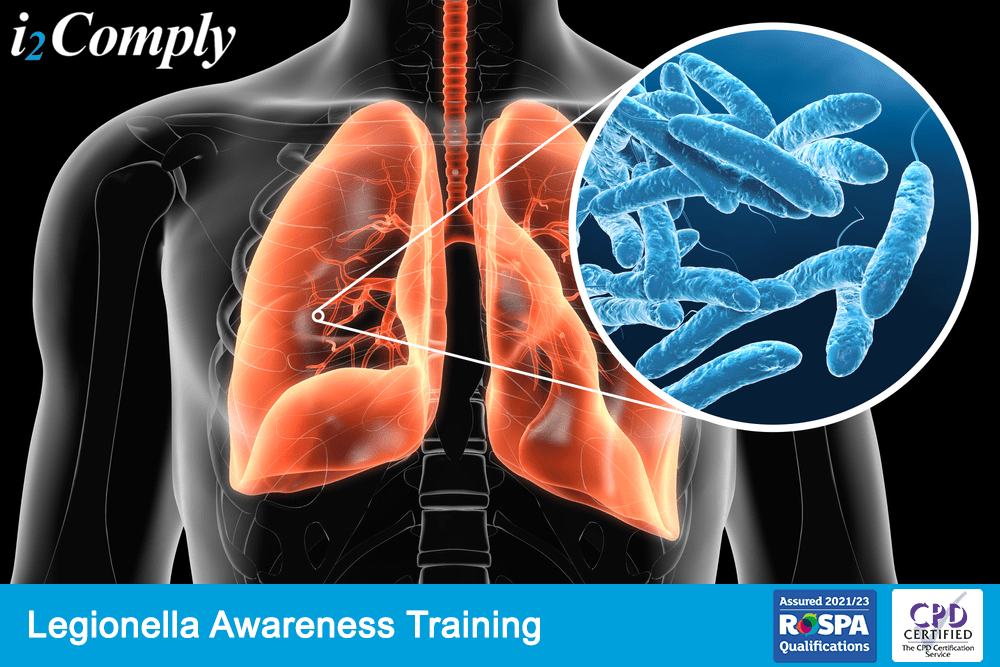
Legionnaires’ disease is a severe form of pneumonia. In other words, it is a lung inflammation that you can get by inhaling small water droplets, containing legionella bacteria. It is uncommon, but it can be very serious. Older adults, smokers and people with weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable to Legionnaires’ disease. Prompt treatment with antibiotics usually cures Legionnaires’ disease. However, some people continue to have problems after the treatment. If untreated Legionnaires’ disease can be fatal.
HSE highlights that lack of training and poor communication are the contributory factors in outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease. Therefore, it is essential that anyone responsible for the management of legionella risks is competent, trained and aware of their responsibilities.
This article explains what legionella is, what UK regulations apply to managing legionella risks and explains how legionella training can help to manage legionella risks in your premises.
What is Legionella?
Legionella is a bacteria found in natural water systems such as rivers, ponds, lakes and reservoirs. This bacterium can cause Legionnaires’ disease, which is a potentially fatal form of pneumonia. Also, legionella can cause less serious conditions such as Pontiac fever and Lochgoilhead fever.
Legionella bacteria mostly occur in the natural water. However, the conditions are rarely suitable for people to get ill from these sources. Actually, legionella outbreaks usually occur due to exposure to the bacteria in human-made water systems, where conditions are right for the bacteria to grow and spread. They include showers, hot tubs, humidifiers, decorative fountains and water features, water heaters, ventilation systems and cooling towers. Also, equipment used in some healthcare settings, such as the waterlines in dental practices, can contain legionella.
What temperature kills legionella?
The ideal water temperature range which allows legionella bacteria to multiply is between 20°C and 45°C.
Below 20°C the bacteria are dormant and if temperatures exceed 60°C the bacteria can not survive.
After legionella grows in a building water system, the bacteria can spread into the air through aerosol or water droplets. Then, people can breathe it in and get Legionnaires’ disease. Less commonly, people can get sick by drinking water that contains Legionella. This happens when water accidentally enters the lungs while drinking. People generally do not spread Legionnaires’ disease to others.
Legionella regulations UK

The employer, or a person in control of the premises, is legally responsible ensure health and safety of their employees and anyone that can be affected by their activities. Also, they need to take reasonable precautions to reduce the risks of exposure to legionella. The regulations that a duty holder or a responsible person must comply with to ensure that the risks of exposure to legionella bacteria are controlled include:
Health and Safety at Work Act etc 1974
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 places a duty on employers or anyone who has control over premises to protect employees or anyone that can be affected by their activities against health and safety risks. The regulations also apply to the risks of exposure to legionella bacteria, which may arise from work activities.
Health & Safety Executive Approved Code of Practice ACOP L8
The Health and Safety Executive’s Approved Code of Practice: Legionnaires’ disease: the control of legionella bacteria in water systems, also known as L8, provides practical guidance on how to manage and control legionella risks. Duty holders, employers and those in control of the premises have a legal responsibility to protect employees and anyone who may affected from health and safety risks. Therefore, they must take appropriate precautions to reduce the risks of exposure to legionella bacteria. Some important duty holder’s responsibilities include:
- Identifying and assessing sources of risk
- Preparing a scheme to prevent or control risk
- Implementing, managing and monitoring precautions
- Keeping and maintaining records of precautions
- Appointing a manager to be responsible for others
The Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (COSHH)
Control of Substances Hazardous to Health Regulations 2002 (COSHH) It is a set of health and safety regulations that places a duty on businesses to protect its employees from harmful substances, including legionella bacteria. COSHH provide a framework of actions designed to assess, prevent, or control the risk that these substances pose and take suitable precautions to keep exposure to a minimum. I2Comply provides COSHH Awareness Training for those interested.
The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999
The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 places a duty on employers and anyone who has control over a workplace to assess the risks that may arise from work activities and cause harm to their employees and others. They must conduct risk assessments to identify the risks to the health and safety of the workforce, decide how they will reduce or control those risks and act upon the risks they identify. The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 apply to controlling the risks of legionella bacteria in the workplace. The legally responsible person must ensure that they or a delegated person conducts a risk assessment and fully implements legionella control measures.
HSG 274 parts 1, 2, 3
Health and Safety Executive provides additional technical guidance in HSG 274. It aims to help duty holders to comply with their legal responsibilities in regard to Legionnaires’ disease.
The guidance includes three parts:
First part is concerned with the control of legionella bacteria in evaporative cooling systems.
Second part is concerned with the control of legionella bacteria in hot and cold water systems.
Third part is concerned with the control of legionella bacteria in other risk systems.
How can awareness training help you to reduce legionella risks?
HSE highlights that lack of training is one of the contributory factors in Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks. Therefore, legionella awareness training is an essential component of managing the risks of legionella in your premises.
As a duty holder or a responsible person, you must be aware of your legal responsibilities and be competent to fulfil them safely and effectively. This equally applies to your legal duties regarding the management of legionella risks. You must have knowledge of Legionnaires’ disease, legionella bacteria and understand how it multiplies and spreads in certain circumstances. Also, you should be aware of how to prevent legionella bacteria from growing and spreading by taking appropriate actions to assess and control the risks.
If a duty holder or a responsible person does not have the correct level of knowledge and competence, they are far more likely to neglect their legionella control duties. As a result, legionella bacteria can be allowed to multiply and spread within a water system, creating a risk of people being exposed to the dangers of the bacteria.
Finally, legionella awareness training provides a great opportunity to review your current processes and understand how you could improve them to increase protection against legionella.
Who should take legionella training?
Generally, everyone working within premises with water systems should attend legionella awareness training. However, the training is particularly useful for anyone who is responsible for water systems on the premises. This includes those who are involved in conducting legionella risk assessments, perform checks on water systems, clean water systems. Also, legionella awareness training is suitable for duty holders, who are usually employers, the self-employed, landlords, letting agents.
Need Legionella Awareness training?
We offer the following RoSPA-assured and CPD-certified online Legionella Awareness Training Course.
Looking for other Health & Safety courses? Take a look at our full range of online Health & Safety courses. If you want to learn more about dealing with hazardous substances in the workplace, you may also be interested in our comprehensive online Asbestos Awareness course.
Have a question?
If you have a question or require more information on any of our training courses. Please contact our friendly support team on 0333 577 5016 or sales@i2comply.com.